Spinnakers aerodynamic coefficients (calculation)

Calculation template
How does it work?
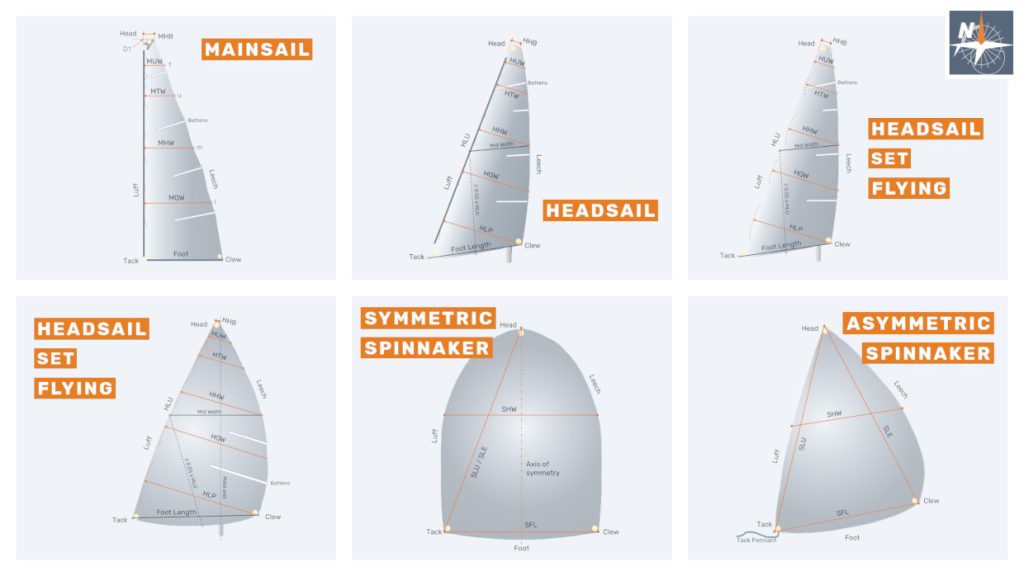
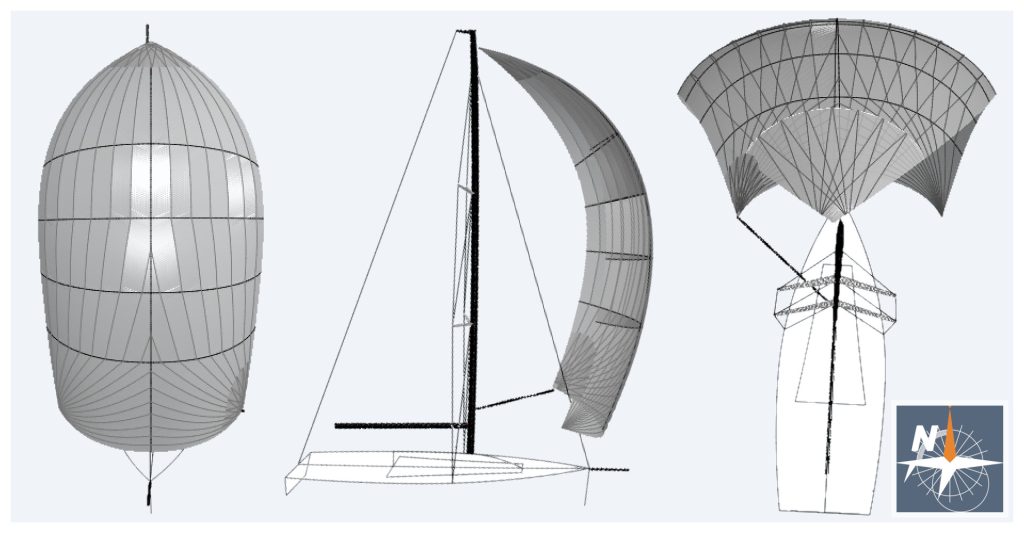
Spinnakers are sails set forward of the mast, or of the foremast mast if there is more than one mast, where the measurement between the half luff point and the half leech point (SHW) is equal or greater than 75% of the foot length (SFL).
| Thrust | Driving Force Coefficients. |
| Side | Heeling Force Coefficients. |
| Lift | Lift Coefficients. |
| Drag Total | Drag Total = Zero-lift Parasite Drag + Induced Drag. The Induced Drag component also includes the effect of the variation of Parasite Drag with lift (Quadratic Parasite Drag). |
| Drag | Drag = Zero-lift Parasite Drag = Friction Drag + Pressure Drag. Parasite Drag is also known as Viscous Drag. Pressure Drag is also known as Form Drag. |
| Eff. span | Effective Height / Reference Height. |
| CE | Height of the Aerodynamic Center of Effort / Reference Height. |
There are two types of spinnakers:
- Symmetric: it is symmetric in shape, material, and cut, about a line joining the head to the center of the foot. It shall not have adjustable leech lines.
- Asymmetric: any spinnaker not qualifying as symmetric.
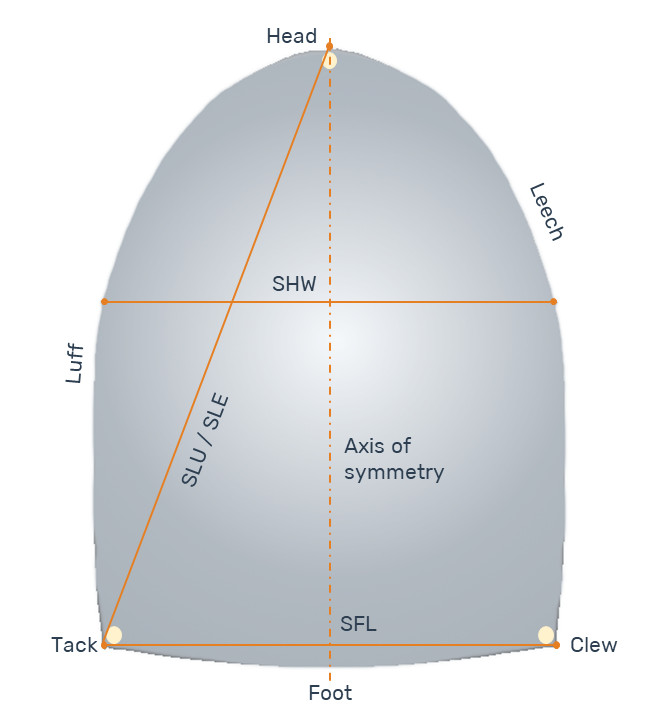
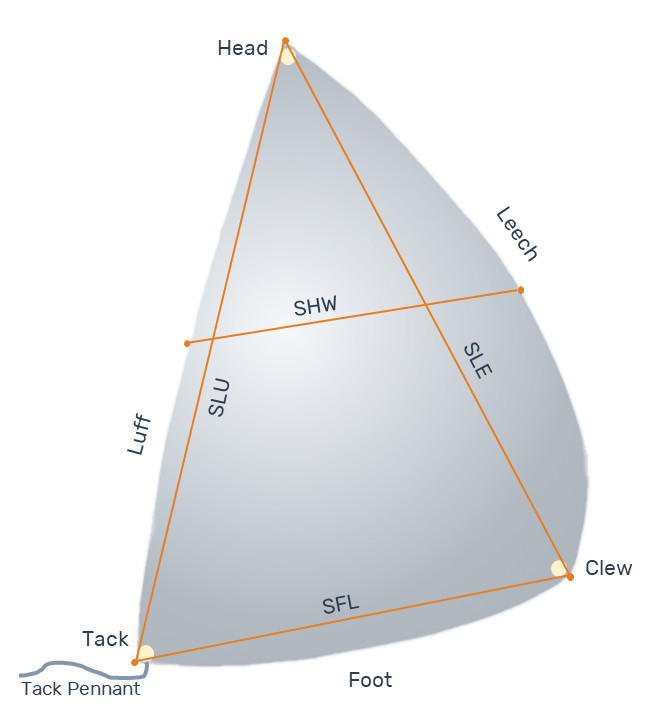
Symmetric spinnakers are considered tacked on a pole, while asymmetric ones can be tacked either on a pole or on the boat’s centerline. The term spinnaker also applies to “gennaker“ which can be considered as an asymmetric spinnaker tacked on the boat’s centerline.
See also:
- International Measurement System: Sails.
- Mainsail aerodynamic coefficients (calculation).
- Headsail aerodynamic coefficients (calculation).
- Headsails “Set Flying” aerodynamic coefficients (calculation).