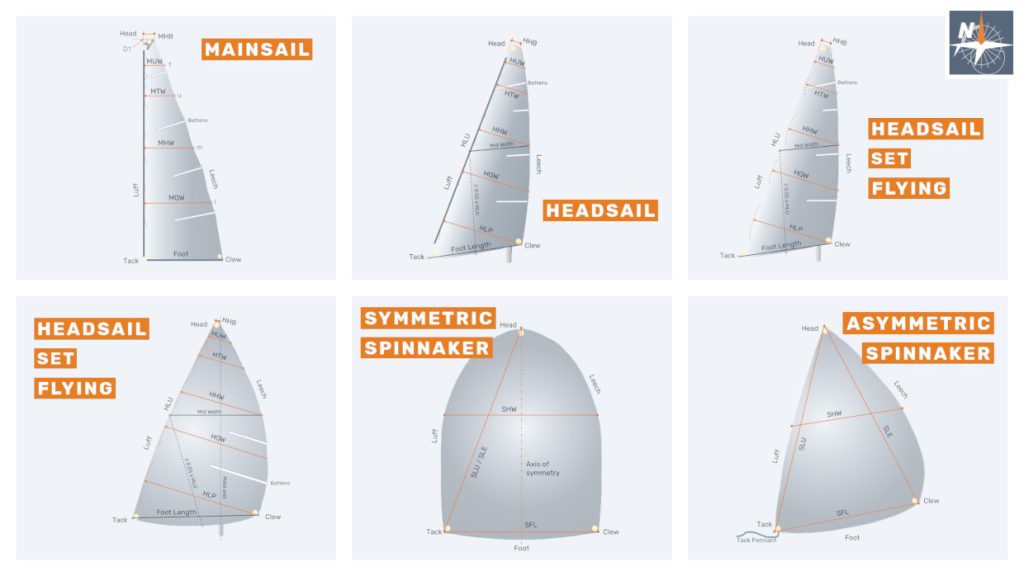
Sails sets: Mainsail + Flying Headsail (calculation)

Calculation template
[navalapp_app charts=’sails_set_flying_headsail_coeffs’ tabs=’yes’ delft=’no’ overview=’no’ aero=’no’ sails_sets=’no’ sails_sets_flying=’yes’ wing=’no’ set_flying=’no’ calculate_button=’yes’ levels=’3,4,5′]
How does it work?
Following the ORC VPP methodology, this template calculation combines the individual sail’s characteristics of a user-defined mainsail and a user-defined flying headsail to produce a set of coefficients that describe the aerodynamic behavior of the entire sails set.
A mainsail is a sail with the luff attached to the mainmast. The mainmast is the only mast in a una rig, sloop rig, or cutter rig, or the fore mast in a ketch rig or yawl rig, or the aft mast in a schooner rig.
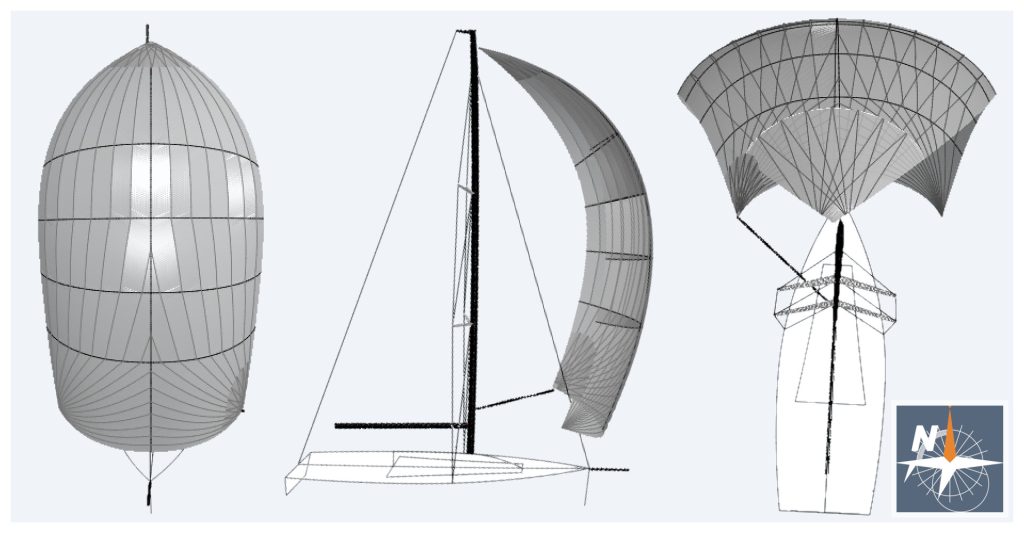
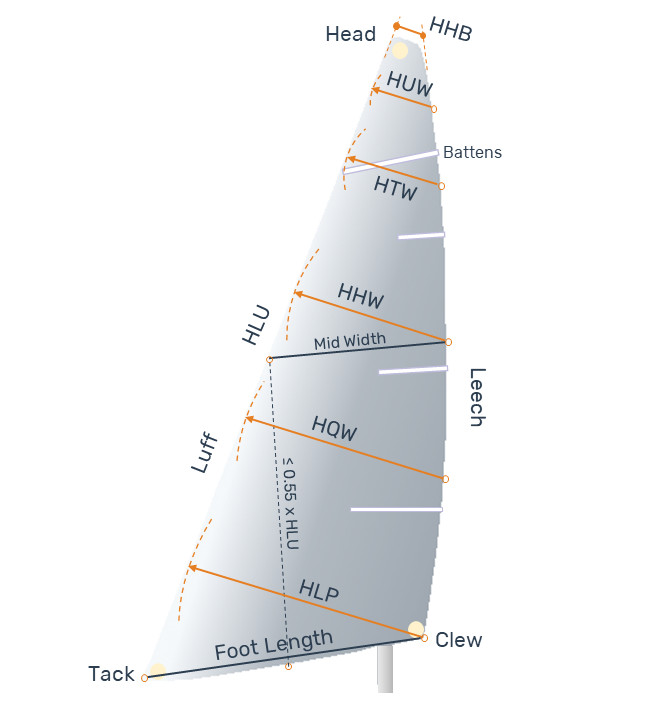
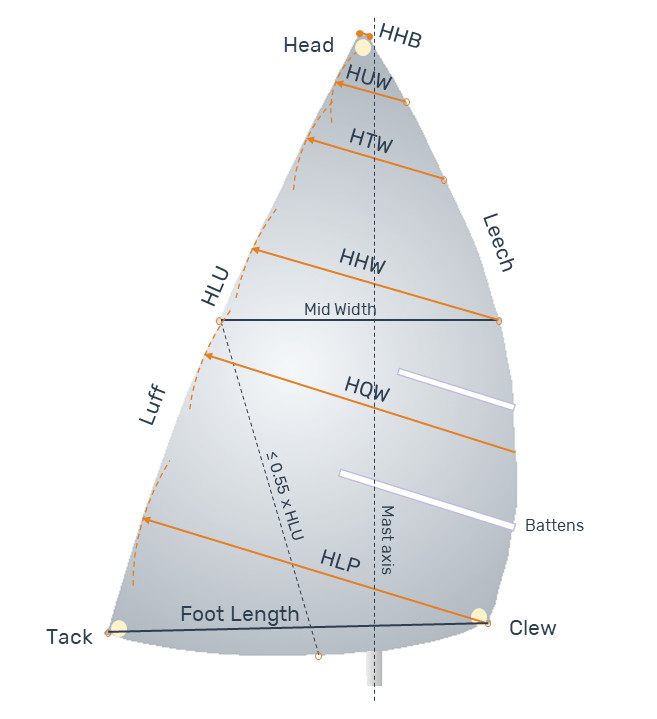
A flying headsail (or headsail set flying) is a sail with no edge attached to the forestay. As it is the case for all headsails, it is set forward of the mast, or the foremast mast if there is more than one mast, and the measurement between the half luff point and the half leech point, known as mid width, must be less than 75% of the foot length (if mid width length ≥ 75% of the foot length, the sail is considered a spinnaker).
There is a wide variety of flying headsails: they can be conceived for close reaching and upwind sailing or designed to give their maximum performance at wider angles. Their performance depends on the ratio HHW/HLP (Headsail Half Width / Headsail Luff Perpendicular), ranging from 50% (jib-like performance) to 85% (spinnaker-like performance).
The template first calculates the lift and the zero-lift parasite drag coefficients and the height of the aerodynamic center of effort of the complete sails set. It also determines the value of the quadratic parasite drag, which is the additional parasite drag generated by the lift.
Then, it calculates the effective height and an efficiency coefficient, both necessary for the computation of the induced drag (drag due to lift) and the total drag coefficient of the sails set.
Finally, the lift and drag aerodynamic coefficients are resolved into two orthogonal forces: the driving force coefficient, thrust, and the heeling force coefficient, side.
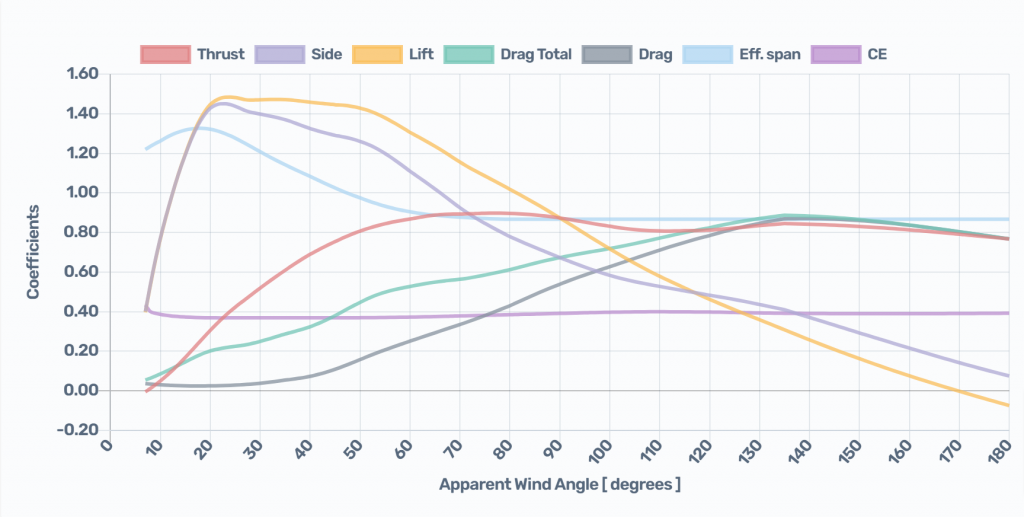
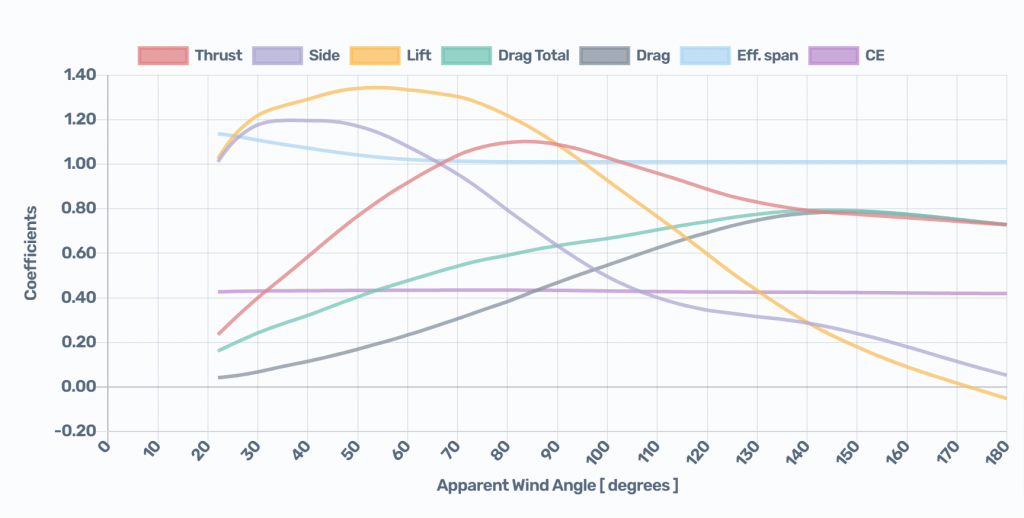
Both the Chart and the Table display the following results calculated for AWA (apparent wind angles) from 0 to 180 degrees:
| Thrust | Driving Force Coefficients. |
| Side | Heeling Force Coefficients. |
| Lift | Lift Coefficients. |
| Drag Total | Drag Total = Zero-lift Parasite Drag + Induced Drag. The Induced Drag component also includes the effect of the variation of Parasite Drag with lift (Quadratic Parasite Drag). |
| Drag | Drag = Zero-lift Parasite Drag = Friction Drag + Pressure Drag. Parasite Drag is also known as Viscous Drag. Pressure Drag is also known as Form Drag. |
| Eff. span | Effective Height / Reference Height. |
| CE | Height of the Aerodynamic Center of Effort / Reference Height. |
The aerodynamic model used in this calculation does not include the windage which is the force generated by the apparent wind on the above-water part of the hull, superstructures, the mast, the rigging wire, and the crew.
See also:
- Sails sets: Mainsail + Headsail (calculation).
- Sails sets: Mainsail + Spinnaker (calculation).
- Mainsail aerodynamic coefficients (calculation).
- Headsails “Set Flying” aerodynamic coefficients (calculation).
- International Measurement System: Sails.


 Navalapp Learn Yacht Design
Navalapp Learn Yacht Design